What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Types of action research
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasizes that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Action research models
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
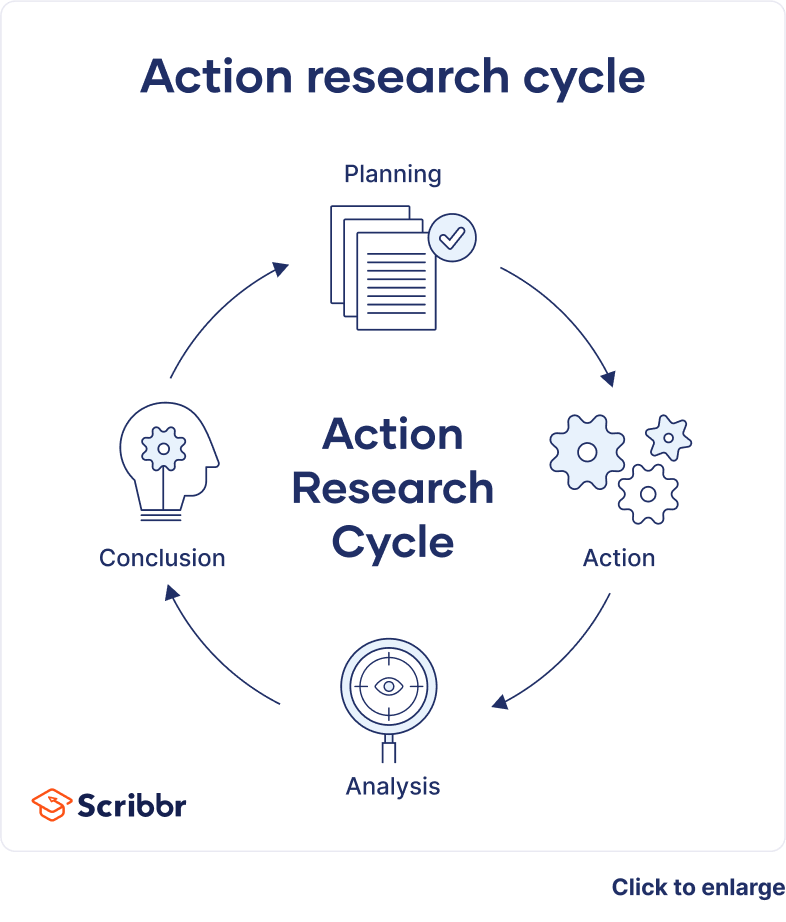
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualized like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualize systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyze existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Examples of action research
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilized, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators.
They found that there had been no change in how chemistry was taught in the last decade—with no incorporation of more modernized teaching approaches or useful online tools. Teachers resolved to implement more modern techniques in their teaching to see if that could improve scores.
Action research vs. traditional research
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative, not summative, and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
| Action research | Traditional research | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
|
|
| Context |
|
|
| Significance |
|
|
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Advantages and disadvantages of action research
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Action research is highly adaptable, allowing researchers to mold their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering, informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalizability and are very difficult to replicate. They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner. Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias, social desirability bias, or other types of cognitive biases.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
Frequently asked questions about action research
- What’s the difference between action research and a case study?
-
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
- What is the main purpose of action research?
-
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
- How is action research used in education?
-
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
- What is a cycle of inquiry?
-
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research. It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
This Scribbr articleGeorge, T. (2023, June 22). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved January 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/action-research/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.